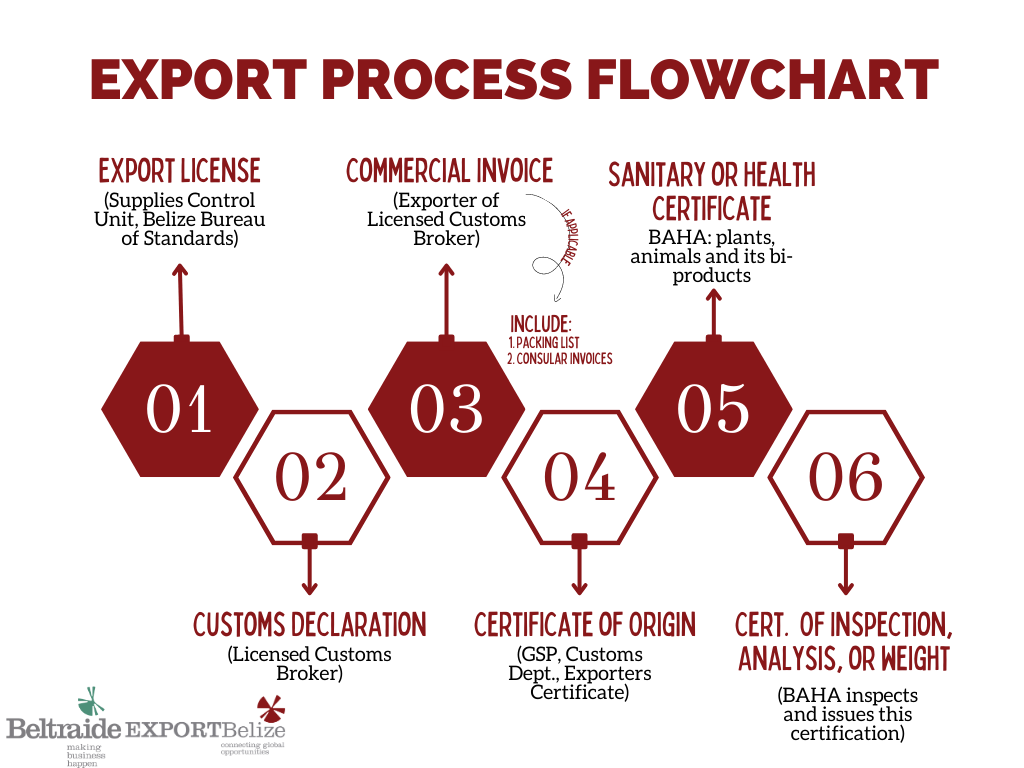
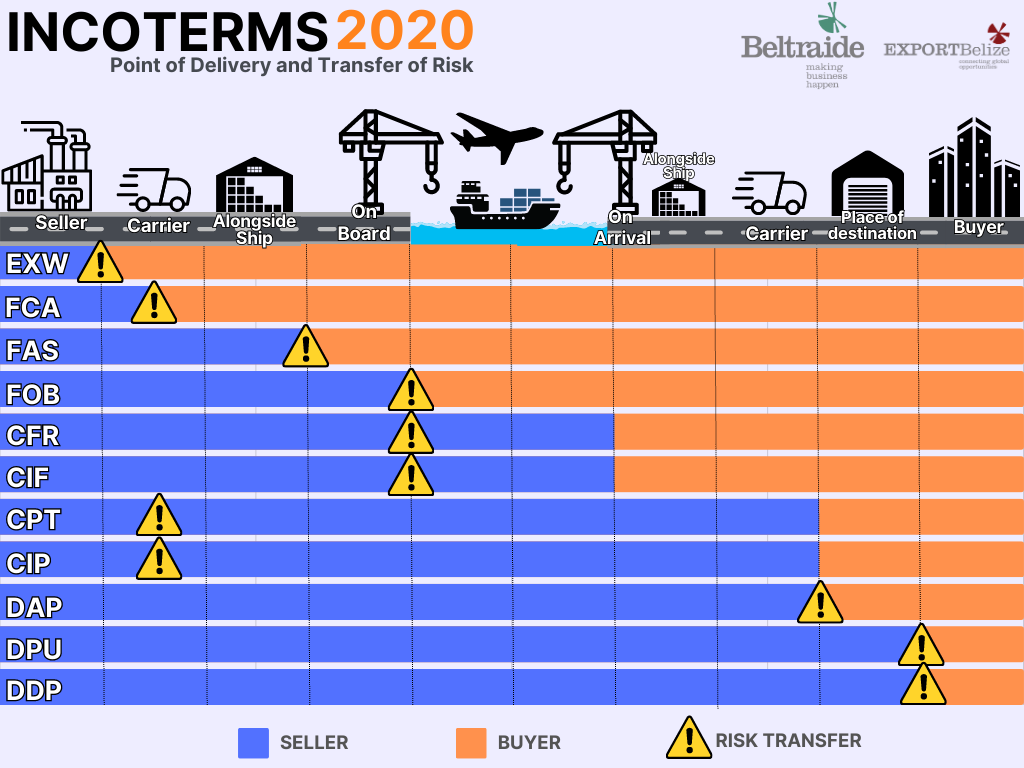
What Are Incoterms?
Inco-terms are international rules for the interpretation of the most commonly used trade terms. They indicate the point at which a shipper, carrier and buyer risks and responsibilities start and end. Each selected Inco-term determines who pays the cost of transportation, loading and unloading of goods and who bears the risk of loss or damage of goods.
There are currently thirteen Inco-terms being used, each categorized by groups. However, the most widely used ones are: Ex-Works, Free on Board, Cost Insurance Freight and Delivery Duty Paid.
There are currently thirteen Inco-terms being used, each categorized by groups. However, the most widely used ones are: Ex-Works, Free on Board, Cost Insurance Freight and Delivery Duty Paid.
EXW: Ex-WORKS
Importers cover the costs under Ex-Works which includes all transportation costs, duties, and insurance, but not that of loading goods onto a truck or vessel or for clearing customs. When an importer makes purchase, he or she must also accept the risks of loss or damage of goods immediately after that purchase.
However, if the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the transportation and insurance costs from the exporter’s premise to the port of export must be added to the Ex-Works price.
Importers cover the costs under Ex-Works which includes all transportation costs, duties, and insurance, but not that of loading goods onto a truck or vessel or for clearing customs. When an importer makes purchase, he or she must also accept the risks of loss or damage of goods immediately after that purchase.
However, if the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the transportation and insurance costs from the exporter’s premise to the port of export must be added to the Ex-Works price.
FCA: FREE CARRIER
Exporters are responsible to clear goods ready for export and deliver them to the carrier specified by the importer; the carrier then loads the goods. Costs for transportation and risk of loss or damage of goods then transfer to the importer.
However, in the case where the exporter is the carrier, he or she must load the goods onto the transport vehicle, but the importer still incurs all costs associated with transporting the goods to their destination.
FAS: FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP
Exporters are responsible to transport the goods from their place of business to the carriage destination, clear the goods for export and place them alongside the vessel at the port of export. However, it is the importer’s responsibility to load the goods onto the vessel and cover all costs involved in shipping the goods to their destination.
FOB: FREE ON BOARD
Exporters are responsible for delivering and loading goods at the carrier’s destination, as well as clearing customs in the country of export. The importer incurs the risk of loss or damage of goods at this point and must also pay for all transportation and insurance costs and clear customs in the country of import destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Cost Insurance and Freight, international freight and insurance costs must be added to the FOB value.
Exporters are responsible to clear goods ready for export and deliver them to the carrier specified by the importer; the carrier then loads the goods. Costs for transportation and risk of loss or damage of goods then transfer to the importer.
However, in the case where the exporter is the carrier, he or she must load the goods onto the transport vehicle, but the importer still incurs all costs associated with transporting the goods to their destination.
FAS: FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP
Exporters are responsible to transport the goods from their place of business to the carriage destination, clear the goods for export and place them alongside the vessel at the port of export. However, it is the importer’s responsibility to load the goods onto the vessel and cover all costs involved in shipping the goods to their destination.
FOB: FREE ON BOARD
Exporters are responsible for delivering and loading goods at the carrier’s destination, as well as clearing customs in the country of export. The importer incurs the risk of loss or damage of goods at this point and must also pay for all transportation and insurance costs and clear customs in the country of import destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Cost Insurance and Freight, international freight and insurance costs must be added to the FOB value.
CFR: COST AND FREIGHT
Exporters are responsible for clearing goods for export, delivering the goods before the ships reach their threshold and incur the international freight charges. However, if goods are loaded after the ships reach their threshold, the importer must assume risk of loss or damage of goods and must also purchase insurance, unload the goods, clear customs and incur all transport cost to deliver the goods to their final destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international freight costs must be deducted from the CFR price.
CIF: COST, INSURANCE AND FREIGHT
Cost Insurance and Freight can be used as an Inco term only when the international transport of goods is partially by water and the transaction must read, “CIF, port of destination.” Under the CIF, exporters are responsible for delivering and loading the goods onto the vessel at the carrier’s location, clear customs in the country of export and purchase insurance. However, the importer must be the beneficiary on the insurance claim.
If goods are loss or damaged during shipment, the importer is responsible to file a claim based on insurance policy obtained from the seller. The importer must also clear customs, pay for any additional transportation and insurance of goods in the country of import.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance and freight costs must be deducted from the CIF price.
CPT: CARRIAGE PAID TO
Using Carriage Paid to, the exporter clears all goods for export, delivers them to the carrier, and pays for carriage cost. The importer then incurs the risk of loss or damage of goods.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international freight cost must be deducted from the CPT price.
CIP: CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO
Carriage and Insurance Paid to is similar to Carriage Paid to. However, not only does the exporter cover the cost for carriage, but also for insurance. That exporter must also transport the goods to the port of export and clear customs. From there on, the importer bears all risk of loss or damage of goods.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, international freight and insurance costs need to be deducted from the CIP price.
Exporters are responsible for clearing goods for export, delivering the goods before the ships reach their threshold and incur the international freight charges. However, if goods are loaded after the ships reach their threshold, the importer must assume risk of loss or damage of goods and must also purchase insurance, unload the goods, clear customs and incur all transport cost to deliver the goods to their final destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international freight costs must be deducted from the CFR price.
CIF: COST, INSURANCE AND FREIGHT
Cost Insurance and Freight can be used as an Inco term only when the international transport of goods is partially by water and the transaction must read, “CIF, port of destination.” Under the CIF, exporters are responsible for delivering and loading the goods onto the vessel at the carrier’s location, clear customs in the country of export and purchase insurance. However, the importer must be the beneficiary on the insurance claim.
If goods are loss or damaged during shipment, the importer is responsible to file a claim based on insurance policy obtained from the seller. The importer must also clear customs, pay for any additional transportation and insurance of goods in the country of import.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance and freight costs must be deducted from the CIF price.
CPT: CARRIAGE PAID TO
Using Carriage Paid to, the exporter clears all goods for export, delivers them to the carrier, and pays for carriage cost. The importer then incurs the risk of loss or damage of goods.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international freight cost must be deducted from the CPT price.
CIP: CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO
Carriage and Insurance Paid to is similar to Carriage Paid to. However, not only does the exporter cover the cost for carriage, but also for insurance. That exporter must also transport the goods to the port of export and clear customs. From there on, the importer bears all risk of loss or damage of goods.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, international freight and insurance costs need to be deducted from the CIP price.
DAF: DELIVERED AT FRONTIER
Importers choose the frontier (the border between the two countries) at which goods will be delivered. Exporters are then responsible for all costs involved in delivering the goods to the named frontier, but the importer incurs all costs for unloading goods, clearing customs and transporting the goods to the final destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance and freight costs must be deducted from the DAF price.
DES: DELIVERED EX-SHIP
Exporters are responsible for all costs involved in delivering goods to the port of destination and bear the risk of loss or damage of goods prior to unloading at the port. However, after goods are being delivered to the importer, that person must unload goods, pay duties, clear customs and provide transportation and insurance to the final destination.
DEQ: DELIVERED EX-QUAY
Exporters are responsible to cover the cost for delivering the goods to the wharf/pier (quay) at the port of destination. The importer is then responsible to cover all costs associated with duties and clearing customs and bear the risk of loss or damage of goods from that point forward.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance, freight costs and cost for unloading the goods must be deducted from the DEQ price.
DDU: DELIVERED DUTY UNPAID
Exporters are responsible to cover the cost for delivery of goods to the port of export. Importers, on the other hand, must ensure that they are responsible for getting the goods loaded onto the vessel and cover costs associated with paying duties, clearing customs and transportation and insurance to the final destination. Importers must also be aware that they bear the risk of loss or damage of goods from the moment goods are being delivered to the port and/or loaded on to the vessel.
DDP: DELIVERED DUTY PAID
A Delivered Duty Paid transaction will read, "DDP named place of destination" and using this, importers chose the port of destination and it is then the exporter’s responsibility to cover the delivery of goods to that port and clear customs in the country of import. That exporter will cover personal cost of delivery because he or she will provide a door-to-door delivery. That exporter will also cover costs associated with clearing customs in both ports of export and destination and therefore, bears all risks of loss or damage of goods until they are delivered to the importer.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Cost Insurance and Freight, the costs of unloading the vessel, clearing customs, and delivery to the importer’s premise in the country of destination, including inland insurance, must be deducted to arrive at the CIF value.
Importers choose the frontier (the border between the two countries) at which goods will be delivered. Exporters are then responsible for all costs involved in delivering the goods to the named frontier, but the importer incurs all costs for unloading goods, clearing customs and transporting the goods to the final destination.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance and freight costs must be deducted from the DAF price.
DES: DELIVERED EX-SHIP
Exporters are responsible for all costs involved in delivering goods to the port of destination and bear the risk of loss or damage of goods prior to unloading at the port. However, after goods are being delivered to the importer, that person must unload goods, pay duties, clear customs and provide transportation and insurance to the final destination.
DEQ: DELIVERED EX-QUAY
Exporters are responsible to cover the cost for delivering the goods to the wharf/pier (quay) at the port of destination. The importer is then responsible to cover all costs associated with duties and clearing customs and bear the risk of loss or damage of goods from that point forward.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Free On Board, the international insurance, freight costs and cost for unloading the goods must be deducted from the DEQ price.
DDU: DELIVERED DUTY UNPAID
Exporters are responsible to cover the cost for delivery of goods to the port of export. Importers, on the other hand, must ensure that they are responsible for getting the goods loaded onto the vessel and cover costs associated with paying duties, clearing customs and transportation and insurance to the final destination. Importers must also be aware that they bear the risk of loss or damage of goods from the moment goods are being delivered to the port and/or loaded on to the vessel.
DDP: DELIVERED DUTY PAID
A Delivered Duty Paid transaction will read, "DDP named place of destination" and using this, importers chose the port of destination and it is then the exporter’s responsibility to cover the delivery of goods to that port and clear customs in the country of import. That exporter will cover personal cost of delivery because he or she will provide a door-to-door delivery. That exporter will also cover costs associated with clearing customs in both ports of export and destination and therefore, bears all risks of loss or damage of goods until they are delivered to the importer.
If the customs valuation in the country of destination where the goods will be transported to is that of Cost Insurance and Freight, the costs of unloading the vessel, clearing customs, and delivery to the importer’s premise in the country of destination, including inland insurance, must be deducted to arrive at the CIF value.
For more information please contact [email protected]